Age-related brain diseases, including conditions such as dementia, stroke, and late-life depression, pose significant challenges to our aging population and overall brain health. Recent research highlights that there are modifiable risk factors that can help mitigate the onset of these diseases. By focusing on lifestyle changes, individuals can actively engage in stroke prevention and minimize dementia causes, thereby improving their quality of life. This is crucial, as the burden of late-life depression often intertwines with these neurological conditions, creating a complex web of health concerns. Understanding the shared risk factors is essential for both prevention and effective treatment strategies.
Cognitive decline and neurological disorders associated with aging are increasingly recognized as pressing public health issues. These conditions, often referred to as age-related brain diseases, encompass a range of ailments such as senile dementia, cerebrovascular accidents, and mental health challenges commonly faced in later years. Recent findings suggest that many of these disorders share underlying risk factors, making them interconnected health concerns. With an emphasis on the importance of lifestyle interventions, individuals are encouraged to adopt healthier habits that can significantly influence their brain function and emotional well-being. Addressing these intertwined issues not only enhances brain health but also fosters a more proactive approach to aging.
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases and Their Shared Risk Factors
Age-related brain diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression are interconnected and influenced by a range of modifiable risk factors. These conditions can significantly affect an individual’s quality of life and pose a challenge for health care systems worldwide. The alarming prevalence of these diseases highlights the importance of understanding common risk factors that can be altered through lifestyle changes. By identifying and addressing these factors, healthcare professionals can help mitigate the incidence of these potentially debilitating brain diseases.
The recent study conducted by researchers at Mass General Brigham sheds light on the shared risk factors present in age-related brain diseases. Factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and poor diet are not only contributors to one condition but impact the others as well. With this vital information, effective prevention strategies can be developed. Understanding the powerful interplay between these diseases emphasizes the need for a comprehensive approach that targets multiple conditions simultaneously, potentially leading to better health outcomes for older adults.
The Role of Modifiable Risk Factors in Stroke Prevention
Stroke prevention is crucial in reducing the health burden posed by age-related brain diseases. The identification of modifiable risk factors such as high blood pressure and obesity offers tangible opportunities for intervention. Simple lifestyle changes—such as improving diet, increasing physical activity, and managing stress—can significantly decrease the likelihood of stroke. For instance, maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains not only supports heart health but can also enhance cognitive function, thereby playing a direct role in preventing stroke.
Additionally, regular physical activity has been shown to be a powerful tool in stroke prevention. It helps regulate blood pressure and improve overall cardiovascular health. The Brain Care Score, developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham, serves as a valuable resource for individuals and healthcare providers aiming to implement strategies that target these modifiable risk factors effectively. By focusing on prevention and lifestyle modifications, individuals can take proactive steps towards reducing their stroke risk.
Dementia Causes and Prevention Strategies
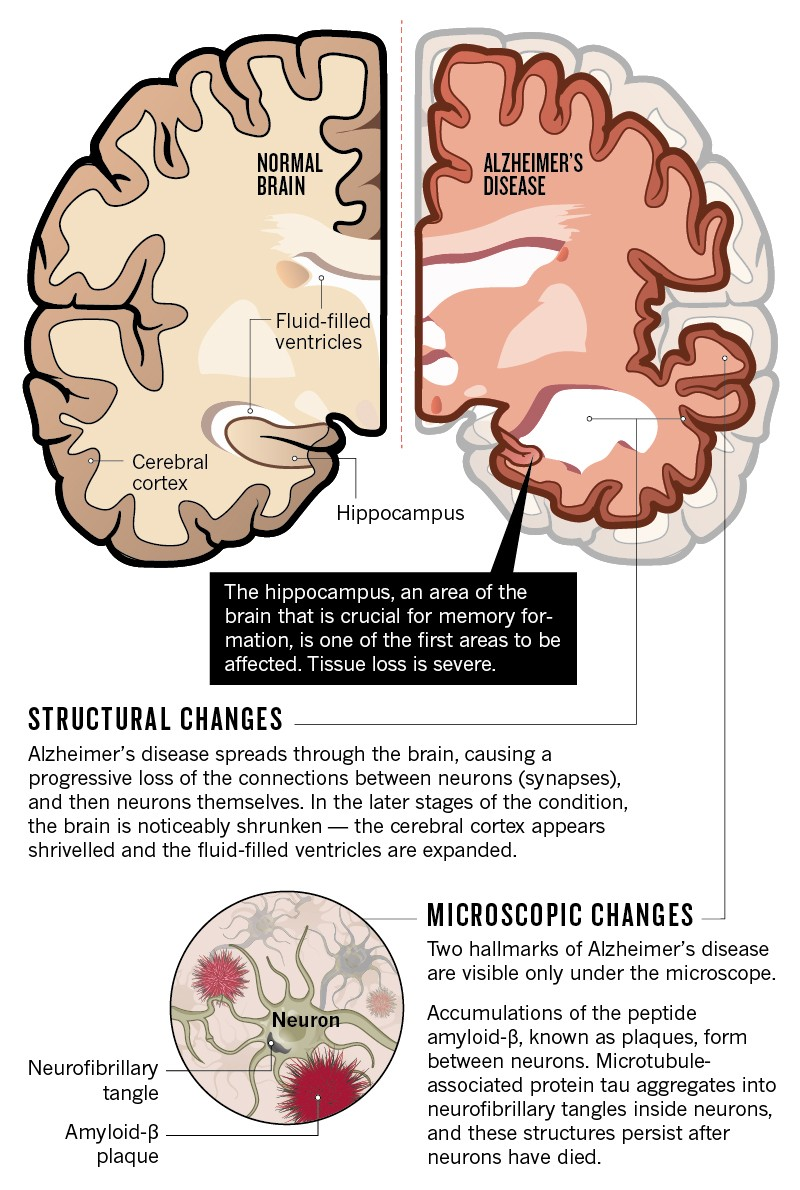
Dementia is a complex condition with various underlying causes, many of which can be influenced by modifiable risk factors. Factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and social engagement levels play critical roles in the development of dementia. The recent findings by Mass General Brigham emphasize the importance of addressing these interconnected factors to prevent dementia onset. For instance, continual social engagement and mental activities can support cognitive health and reduce the likelihood of dementia by keeping the brain active and healthy.
Moreover, the recognition of lifestyle modification as a critical preventive measure is essential. Engaging in regular exercise, consuming a brain-healthy diet, and managing chronic diseases can create a protective effect against dementia. The shared risk factors across different conditions highlight the potential for comprehensive prevention strategies that address multiple diseases at once. By shifting the focus from treatment to prevention, it is possible to significantly lower the incidence of dementia.
Addressing Late-Life Depression as a Shared Risk Factor
Late-life depression is not only a significant health concern by itself but also a substantial risk factor for other age-related brain diseases, including dementia and stroke. Understanding the interplay between depression and these conditions is crucial, as untreated depression can worsen the prevalence and impact of stroke and dementia. Mental health matters are closely tied to the state of one’s brain health; thus, addressing depression through appropriate interventions can also mitigate risks associated with other conditions.
Open discussions about mental health, along with an active approach to managing modifiable risk factors such as stress and social engagement, can lead to meaningful improvements in late-life depression. As identified in current research, fostering social connections and creating a purpose in life are not just beneficial for emotional well-being but also play an essential role in protecting brain health. Healthcare systems are encouraged to incorporate mental health strategies into preventive care protocols for older adults.
The Importance of Lifestyle Changes for Brain Health
Implementing lifestyle changes is essential to improving brain health and preventing age-related brain diseases. Factors such as diet, exercise, and social interaction significantly contribute to brain health. A balanced diet low in processed foods and rich in nutrients can enhance brain function, while regular physical activity promotes healthy circulation and cognitive function. Such lifestyle modifications not only improve overall well-being but also lower the risk of diseases like stroke and dementia.
Furthermore, engaging in mentally stimulating activities such as problem-solving and social interactions can keep the brain agile. The implications of these lifestyle changes are profound, as they can potentially reshape the landscape of brain disease prevention. Increasing awareness of the interconnected risk factors allows individuals to make informed choices that benefit their cognitive health throughout aging.
The Role of Healthcare in Preventing Age-Related Brain Diseases
Healthcare providers play a vital role in the prevention of age-related brain diseases by helping patients understand their risk factors. With the identification of shared modifiable factors, healthcare systems can design comprehensive preventative strategies that include patient education on lifestyle changes. Such proactive approaches can help reduce the incidence of conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, emphasizing the interconnected nature of these diseases.
Moreover, implementing interventions based on the Brain Care Score can guide healthcare practices in providing personalized care. By measuring patients’ lifestyles and health profiles, healthcare providers can assist in identifying areas for improvement, thus empowering patients to adopt healthier habits that contribute to brain health. The collaboration between patients and healthcare professionals is essential in creating tailored plans that not only address individual risk factors but also foster a holistic approach to overall wellness.
Recent Innovations in Brain Health Measurement
Recent advancements in measuring brain health are exemplified by the development of tools such as the Brain Care Score. This score aims to provide a comprehensive overview of an individual’s risk factors associated with age-related brain diseases. Through simple assessments, healthcare providers can identify critical areas of concern that need addressing. The score is an innovative step toward recognizing the significance of modifiable risk factors and tailoring preventive strategies.
As more research emerges, it becomes increasingly evident that early intervention can prevent the onset of serious brain health issues. The Brain Care Score is intended to empower both healthcare providers and patients by providing clear benchmarks to work towards in lifestyle adjustments. With ongoing validation, such tools can transform how we manage and prevent age-related brain diseases, ensuring that informed decisions are made effectively.
The Impact of Chronic Conditions on Brain Health
Chronic conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes are intricately linked to age-related brain diseases. These conditions can exacerbate risks for stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, creating a cycle that is difficult to break. For example, managing blood pressure through diet and exercise can significantly reduce the risk of stroke and improve overall brain health. Recognizing these connections allows for better management of chronic conditions with a multi-faceted approach.
It’s essential for healthcare providers to monitor and treat chronic conditions effectively as part of comprehensive brain health care. By addressing these underlying health issues, clinicians can mitigate the onset of age-related brain diseases and enhance the quality of life for their patients. Therefore, a focused approach on chronic conditions is crucial in the overarching strategy of preventing diseases like dementia and stroke.
Creating Social Support Networks for Brain Health
Social engagement is a powerful protective factor against age-related brain diseases. Lacking social support can increase the risk of conditions such as late-life depression and cognitive decline. Thus, fostering community support systems that encourage social interaction is vital. Programs that connect older adults with peers not only enhance emotional well-being but also create a robust framework for brain health.
Moreover, encouraging participation in social activities addresses several modifiable risk factors identified by researchers at Mass General Brigham. Engaging in group activities, volunteering, or joining clubs can significantly improve quality of life and cognitive health for older adults. As these social networks develop, they offer a buffer against the risks associated with isolation and depression, ultimately promoting better brain health outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some common modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases?
Recent studies have identified several modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases, including high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease, poor diet, and excessive alcohol use. Addressing these factors can significantly lower the risk of conditions like stroke, dementia, and late-life depression.
How can diet influence the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Diet plays a crucial role in brain health and can impact the risk of age-related brain diseases. A poor diet, particularly one high in processed foods and sugars, can increase the likelihood of developing conditions such as stroke, dementia, and depression. Conversely, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can help mitigate these risks.
What role does physical activity play in preventing age-related brain diseases?
Physical activity is a significant modifiable risk factor for age-related brain diseases. Regular exercise helps improve blood circulation, reduces stress, and enhances overall mental health, which can lower the risk of stroke, dementia, and depression. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity weekly is recommended.
Can social engagement reduce the risk of dementia and depression in older adults?
Yes, social engagement is a vital factor in maintaining brain health. A lack of social interaction can lead to isolation and increase the risk of late-life depression and dementia. Staying socially active can help boost cognitive function and emotional well-being, thereby reducing the risk of age-related brain diseases.
What is the relationship between hypertension and age-related brain diseases?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a major risk factor for age-related brain diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. Managing blood pressure through lifestyle changes and medication can significantly reduce the incidence of these conditions, improving overall brain health.
How does stress impact the development of age-related brain diseases?
Chronic stress is linked to an increased risk of various age-related brain diseases, including depression and dementia. High levels of stress can negatively affect brain function and overall mental health, making stress management techniques essential for protecting against these conditions.
What is the significance of the Brain Care Score in relation to age-related brain diseases?
The Brain Care Score is a tool developed by researchers to assess an individual’s efforts in protecting brain health. It incorporates various modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases, helping individuals understand their risk profile and guiding them on how to improve their brain health effectively.
What types of interventions can help reduce the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Interventions such as adopting a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and increasing social engagement can significantly lower the risk of age-related brain diseases. These lifestyle changes address multiple shared risk factors, providing a comprehensive approach to improving brain health.
| Key Factor | Impact on Age-Related Brain Diseases |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Increases risk of stroke, dementia, and depression. |
| Blood Pressure | Major risk factor for all three conditions. |
| Kidney Disease | Increases risk of stroke, dementia, and depression. |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | High levels are a risk factor for these conditions. |
| Total Cholesterol | High levels increase the risk of stroke and dementia. |
| Alcohol Use | Excessive consumption linked to increased risk. |
| Diet | A poor diet can contribute to the development. |
| Hearing Loss | Modifiable risk factor for dementia. |
| Pain | Chronic pain can increase depression risk. |
| Physical Activity | Lack of activity is a risk for all three conditions. |
| Purpose in Life | A lack can lead to depression risks. |
| Sleep | Poor quality increases depression risk. |
| Smoking | Major risk factor for all three conditions. |
| Social Engagement | Lack contributes to greater depression risk. |
| Stress | Chronic stress increases depression risk. |
| Depression | Untreated may increase risks of other conditions. |
| Obesity | A risk factor for all three conditions. |
Summary
Age-Related Brain Diseases, such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, are interconnected conditions with significant implications for individuals’ health. Recent findings have revealed that there are 17 modifiable risk factors that can lower the likelihood of developing these conditions. By addressing issues like high blood pressure, chronic kidney disease, and lifestyle choices such as diet and physical activity, it is possible to reduce risks significantly. The interconnected nature of these diseases suggests that preventive measures could lead to a comprehensive decrease in incidence, helping individuals maintain better brain health as they age. This emphasizes the importance of awareness and intervention in managing age-related brain diseases.