Maternal mortality in the U.S. continues to be a pressing issue, as recent studies reveal that it ranks the highest among high-income countries, with pregnancy-related deaths rising alarmingly. Alarmingly, over 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, emphasizing the urgent need for better maternal healthcare. Significant disparities exist, particularly across racial and ethnic lines, complicating the landscape of maternal health disparities. Improving prenatal care and postpartum care is crucial to addressing chronic medical conditions during pregnancy, which increasingly affect younger individuals. To combat these troubling trends, focused efforts on systemic healthcare improvements and targeted interventions are imperative.
The ongoing crisis surrounding maternal mortality in America encompasses a myriad of issues, including rising rates of pregnancy-related fatalities and persistent health inequities. With an urgent need to enhance maternity care frameworks, it is essential to understand the nuances of the U.S.’s maternal health challenges. Comprehensive approaches to prenatal and postpartum care are needed, particularly as chronic health issues increasingly impact expectant mothers. Furthermore, acknowledging the significant racial and ethnic disparities within maternal health outcomes is vital for future policy formulations. As policymakers and healthcare providers navigate this challenging landscape, it is critical to prioritize maternal wellbeing and implement effective strategies to reduce mortality rates.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
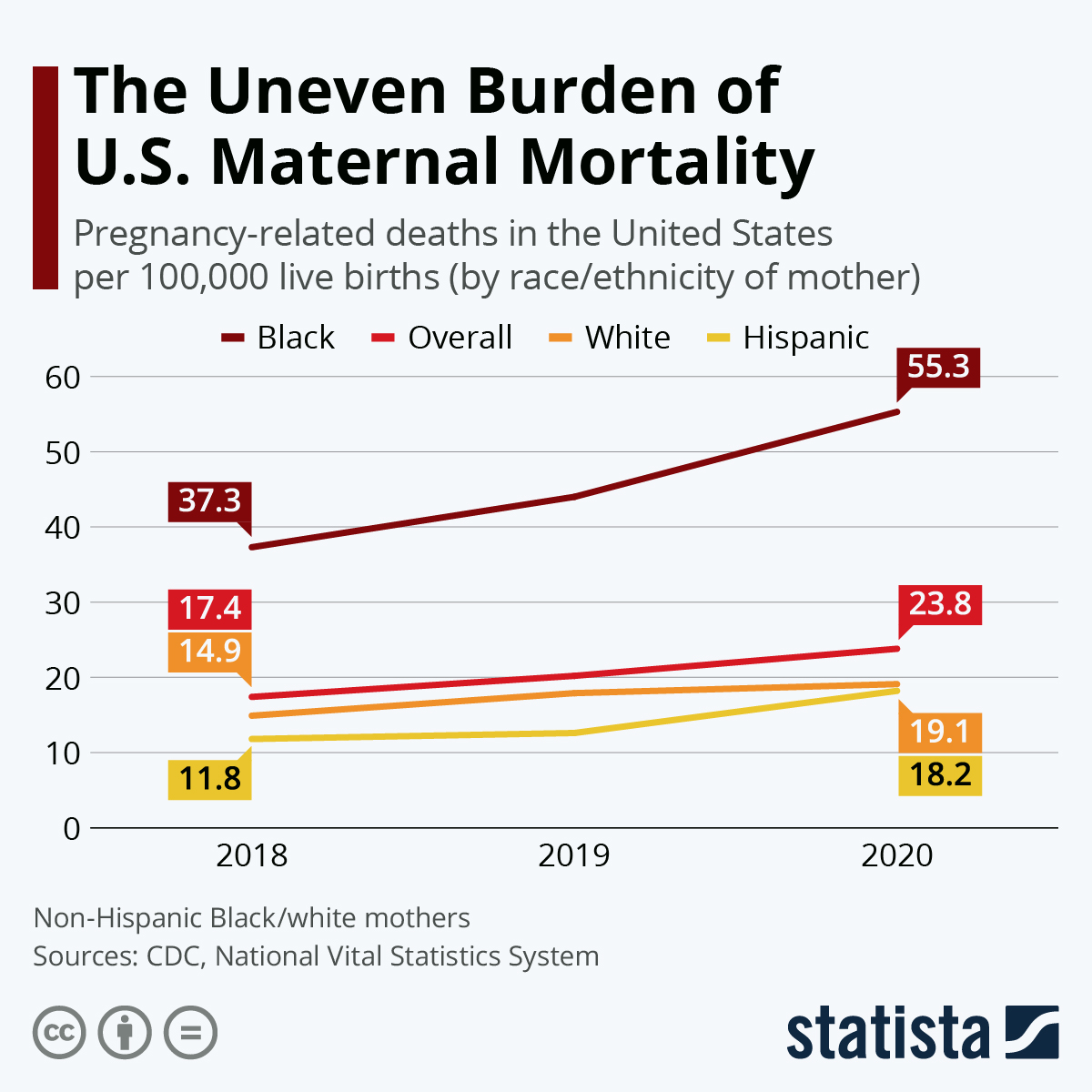
Maternal mortality rates in the United States are alarmingly high, particularly when compared to other high-income countries. In 2022, the U.S. recorded 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, a stark increase from 25.3 deaths per 100,000 in 2018. This raises serious questions about the effectiveness of the healthcare system and the accessibility of quality prenatal care for all women. As the data illustrates, the majority of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, highlighting a critical need for systemic improvements in maternal healthcare.
Disparities in maternal mortality rates also reflect a deep-rooted problem within the U.S. healthcare framework. For instance, American Indian and Alaska Native women face a mortality rate of 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, which is nearly four times higher than that of white women. This disparity underscores the imperative to address maternal health disparities through targeted interventions that ensure equitable access to care, particularly for marginalized populations.
The Role of Chronic Medical Conditions in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Chronic medical conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease are significantly linked to the rising maternal mortality rates in the U.S. As women of reproductive age increasingly face these health challenges, the risk of pregnancy-related deaths escalates. Researchers have noted that there is a worrying trend of younger women, particularly those aged 25 to 39, experiencing elevated rates of hypertension and related cardiovascular issues during pregnancy. This shift in health trends highlights the urgent need for improved prenatal care that focuses on the pre-existing health conditions of expectant mothers.
Furthermore, addressing these chronic conditions requires a comprehensive approach that not only prioritizes maternal health during pregnancy but also emphasizes continuous postpartum care improvement. As noted in studies, maternal mortality is not solely a pregnancy issue; it extends into the postpartum period, necessitating ongoing monitoring and management of chronic conditions that could pose risks to a mother’s health even after childbirth.
The Importance of Prenatal and Postpartum Care
Quality prenatal care is essential for monitoring the health of both mother and child during pregnancy. The findings indicate that much of the pregnancy-related mortality can be mitigated through better access to prenatal services that are comprehensive and culturally competent. This includes routine screenings for chronic conditions, individualized care plans, and education about health risks associated with pregnancy. Moreover, healthcare systems must prioritize establishing support frames that empower women to seek timely interventions.
On the other hand, postpartum care is equally crucial in reducing maternal deaths that occur after childbirth. Unlike many other countries, the U.S. has historically offered limited support beyond the early postpartum period, failing to monitor women adequately until their next pregnancy. The conversation around extending postpartum healthcare access and building robust follow-up services is vital for preserving maternal health. This acknowledgment can lead to necessary policy reforms that ensure all mothers receive critical support throughout the entire continuum of care.
Policy Recommendations for Addressing Maternal Health Disparities
To address the escalating maternal mortality rates in the U.S., comprehensive policy reforms are urgently needed. Policymakers must target systemic changes in maternal healthcare policy, particularly focusing on reducing health disparities faced by minority groups such as African American and Native American women. Innovative solutions, such as community-based health initiatives and telehealth, should be championed to improve access and education around maternal health.
Simultaneously, there should be a push for increased funding for maternal health research and public health infrastructure. Advocacy for women’s health issues needs to rise in priority on the political agenda, pushing to ensure adequate resources are allocated for maternal health programs that support disparities in care. This could make a significant difference in shaping policies that aim to reduce preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
COVID-19 Impact on Maternal Mortality Rates
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced added risks to maternal health, contributing significantly to the rise in pregnancy-related deaths. The initial onset of the pandemic saw sharp increases in maternal mortality, primarily due to overwhelmed healthcare systems and reduced access to vital care services. Many women faced delays in receiving prenatal and postpartum care during the pandemic, contributing to worsened outcomes for both mothers and infants.
As we recover from the pandemic, addressing the implications for maternal health is critical. Healthcare systems must learn from the vulnerabilities exposed during this period, ensuring a resilient framework is built around maternal services that can withstand future public health crises. Investing in robust telehealth options and ensuring mothers feel supported in accessing care can help mitigate risk factors that have surged due to pandemic pressures.
Advocating for Better Maternal Healthcare Infrastructure
Building a stronger maternal healthcare infrastructure is essential in combating the rise in maternal mortality rates throughout the United States. Current systems must evolve to provide comprehensive support for women, ranging from prenatal education to postpartum care. With the incorporation of modern technology and community outreach programs, healthcare professionals can enhance patient experiences and outcomes by ensuring that all women have equal access to high-quality care.
Furthermore, there should be a dedicated effort to improve healthcare delivery systems and policies that specifically prioritize maternal health. Investments in public health initiatives focused on maternal care can yield significant long-term benefits for communities, limiting preventable pregnancy-related deaths. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, policymakers, and community leaders can pave the way for innovative solutions that address the systemic barriers facing pregnant women today.
The Significance of Late Maternal Deaths
Late maternal deaths, defined as those occurring between 42 days and one year after childbirth, present a crucial aspect of understanding maternal mortality. Currently, these deaths are often overlooked in maternal health statistics, despite accounting for nearly one-third of total maternal deaths. Recognizing the significance of late maternal deaths prompts a reevaluation of how healthcare systems approach postpartum care, emphasizing the need for extended monitoring and support beyond the immediate postpartum period.
Incorporating late maternal deaths into policy discussions can lead to a broader recognition of the continuum of maternal health. As healthcare providers begin to adapt their practices to offer ongoing support and interventions during the year following childbirth, the focus can shift toward establishing systematic care practices that manage chronic conditions and address mental health issues. These approaches can significantly enhance the quality of care and even reduce the rates of maternal mortality associated with long-term complications.
Addressing Maternal Health Disparities Through Education and Awareness
Raising awareness and educating communities about maternal health disparities is paramount in creating meaningful change. By ensuring that women have access to information about their health rights, available resources, and the importance of seeking care, we can empower them to advocate for themselves and others. Programs aimed at increasing literacy around maternal health issues can help bridge the gaps faced by vulnerable populations and decrease instances of preventable deaths.
Additionally, educational initiatives need to involve healthcare providers, training them to recognize and dismantle biases that contribute to health disparities. Continued education on cultural competency and equitable care is essential in ensuring that all women receive fair treatment regardless of their background. Creating a compassionate healthcare environment will not only improve patient experiences but also help counteract the systemic issues that contribute to the social determinants of health affecting maternal outcomes.
Integrating Community-Based Approaches to Support Maternal Health
Community-based approaches to maternal healthcare can play a transformative role in reducing pregnancy-related mortality. By harnessing local resources and support systems, healthcare providers can develop tailored interventions that meet the specific needs of their diverse populations. Programs that promote partnerships with community organizations can enhance outreach and provide essential services that empower women throughout pregnancy and postpartum.
Furthermore, integrating peer support systems and mentorship for new mothers can significantly improve outcomes by creating a network of support that women can rely upon. Community health workers can help navigate the healthcare system, provide education on pregnancy-related issues, and foster connections with local services. Empowering communities to take an active role in maternal health will ultimately aid in bridging the gap caused by healthcare disparities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is primarily driven by conditions such as cardiovascular disease, hemorrhage, and infections. Chronic medical conditions like hypertension and diabetes also significantly contribute. Improved prenatal and postpartum care can greatly reduce these preventable pregnancy-related deaths.
How do maternal health disparities affect pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S.?
Maternal health disparities significantly impact pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S., with women of color, particularly American Indian, Alaska Native, and non-Hispanic Black women, facing much higher mortality rates. Addressing these disparities requires targeted policies and improved access to quality prenatal and postpartum care.
What role does prenatal care play in reducing maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Prenatal care is crucial in identifying and managing risks during pregnancy, thereby playing a vital role in reducing maternal mortality in the U.S. Early and regular prenatal visits can help detect chronic medical conditions and prevent complications, significantly lowering the rates of pregnancy-related deaths.
What improvements are being suggested for postpartum care to decrease maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Postpartum care improvements include extending the coverage duration beyond the traditional six weeks and implementing consistent follow-up for all mothers. Recognizing late maternal deaths, which occur from 42 days to one year postpartum, is essential in enhancing maternal health services and addressing the ongoing risks.
How do chronic medical conditions impact maternal mortality rates during pregnancy?
Chronic medical conditions, such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease, have a profound impact on maternal mortality rates during pregnancy in the U.S. The rising prevalence of these conditions among younger individuals increases the risk of pregnancy-related deaths, highlighting the need for better management and care.
What systemic changes are needed to address the high maternal mortality rate in the U.S.?
To address the high maternal mortality rate in the U.S., systemic changes such as increasing healthcare access, implementing equitable policies, and enhancing the quality of prenatal and postpartum care are essential. Investment in public health infrastructure and targeted interventions can help close the disparities and reduce preventable deaths.
Why is it important to count late maternal deaths in maternal mortality statistics?
Counting late maternal deaths, which occur between 42 days and one year postpartum, is important for understanding the full scope of maternal mortality in the U.S. It reflects the need for ongoing care and support beyond the immediate postpartum period, helping to inform strategies to prevent these deaths.
What impact does pregnancy-related death have on communities in the U.S.?
Pregnancy-related deaths have a substantial impact on communities in the U.S., affecting family structures, economic stability, and increasing health disparities. These deaths often highlight systemic issues within healthcare and the need for comprehensive maternal health initiatives to protect women’s lives.
How can states with high maternal mortality rates learn from states with lower rates?
States with high maternal mortality rates can learn from those with lower rates by analyzing effective policies, healthcare practices, and community-based interventions. Sharing best practices and investing in comprehensive prenatal and postpartum care can help reduce disparities and improve maternal outcomes.
What are the statistics on maternal mortality rates during the COVID-19 pandemic in the U.S.?
During the COVID-19 pandemic, maternal mortality rates rose sharply, particularly in 2021. Data from 2018 to 2022 indicated that the U.S. maternal mortality rate increased from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births, reflecting the pandemic’s impact on healthcare access and maternal health outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Preventability of Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths in the U.S. are preventable. |
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rate | The U.S. has the highest maternal mortality rate among high-income countries, with rates rising from 25.3 to 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births between 2018 and 2022. |
| Disparities by Race and Ethnicity | American Indian and Alaska Native women face the highest rates at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births, followed by non-Hispanic Black women (76.9) and white women (27.6). |
| COVID-19 Impact | The sharpest increase in maternal mortality occurred in 2021, likely due to the COVID-19 pandemic. |
| Chronic Diseases | Cardiovascular diseases account for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths, with rising rates among younger women. |
| Need for Improved Care | Investments are required in public health infrastructure and prenatal/postpartum care to reduce mortality rates. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly one-third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days and one year postpartum. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. remains a critical public health concern, with high rates and significant disparities among different racial and ethnic groups. Despite advances in healthcare, more than 80 percent of these deaths are preventable, yet the U.S. continues to lead high-income nations in maternal mortality. Recent data highlights the need for comprehensive improvements in prenatal and postpartum healthcare services, particularly in addressing chronic diseases and systemic inequities that contribute to these troubling statistics. Moving forward, it is vital to advocate for stronger public health policies and infrastructure that prioritize maternal health to create meaningful change.