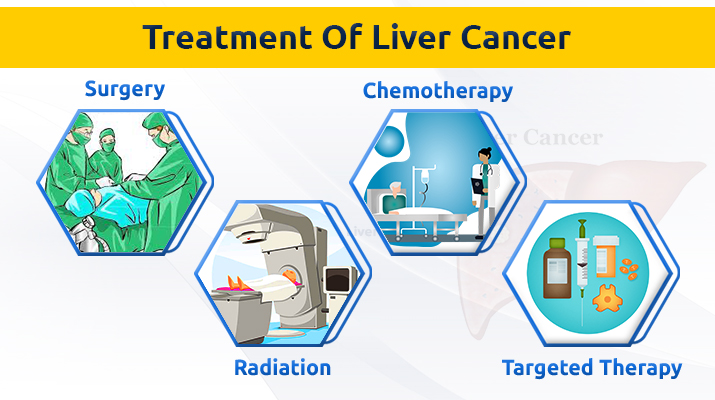
Liver cancer treatment is evolving as researchers uncover the intricate connections between bile imbalance and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most prevalent form of liver cancer. Recent studies highlight how disruptions in bile acid metabolism can instigate liver damage and ultimately lead to cancer formation. A pivotal discovery regarding the FXR function reveals that it may serve as a crucial target for therapeutic interventions, offering hope for new treatment strategies. The activation of YAP, a key regulator in this process, has also been linked to poor outcomes, further emphasizing the need for detailed understanding of bile dynamics. As the medical community delves deeper into these molecular pathways, the potential for innovative liver cancer treatments becomes increasingly promising.
The management of liver malignancies, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, is undergoing significant advancements fueled by groundbreaking research into bile acid dysregulation. By understanding how the liver processes bile and the hormonal-like activity of bile acids, scientists are unraveling the complexities of liver health and disease. This fresh perspective on the interplay between bile metabolism and cancer pathogenesis not only enhances our grasp of liver function but also opens avenues for developing effective therapeutic modalities. Ultimately, addressing the disruptions in bile production and metabolism could pave the way for revolutionary approaches to combat liver cancer and improve outcomes for patients.
Understanding Bile Imbalance and Its Link to Liver Cancer
Bile imbalance plays a crucial role in the onset of liver diseases, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), which is the most prevalent form of liver cancer. This disruption in bile acid metabolism can lead to significant health complications, as bile acids are not merely digestive agents; they also function as hormones that regulate various metabolic processes. When the balance of bile acids is altered, it triggers a cascade of cellular events that can culminate in liver injury and inflammation, paving the way for cancer development.
The study led by Yingzi Yang emphasizes the delicate regulatory mechanisms governing bile production and the dire consequences of its disruption. By pinpointing a critical molecular switch, the research reveals how the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway can affect bile acid dynamics, resulting in the progression towards HCC. Understanding these intricate relationships provides insight into potential therapeutic interventions that could mitigate the risk of liver cancer.
The Role of YAP Activation in Tumor Development
YAP (Yes-associated protein) activation has emerged as a pivotal player in tumor formation, particularly in relation to bile acid regulation. Contrary to expectations that YAP would promote cell growth, it has been found to act as a repressor, disrupting the function of FXR, a key bile acid sensor. This repression leads to an overproduction of bile acids, which accumulate in the liver and contribute to conditions like fibrosis and inflammation, ultimately increasing the risk of developing liver cancer.
The study’s findings suggest that targeting YAP’s repressive effects on FXR could present a novel therapeutic approach to prevent liver cancer progression. By enhancing FXR function or promoting the excretion of bile acids, researchers are exploring ways to disrupt this harmful cycle. Such pharmacological strategies not only aim to lower the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma but also underscore the importance of understanding bile acid metabolism within cancer biology.
Targeting FXR Function for Liver Cancer Treatment
The Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is integral in maintaining bile acid homeostasis, making it a critical target for liver cancer treatment strategies. With the discovery that YAP activation hinders FXR function, researchers are investigating ways to enhance FXR’s activity. By activating FXR pharmacologically, it is possible to counteract the harmful effects of excessive bile acids and their contribution to liver cancer pathogenesis.
Innovative research approaches have already shown promise in experimental models where FXR activation or inhibition of YAP’s repression can significantly reduce liver damage and slow cancer progression. This breakthrough represents a shift towards more targeted interventions that consider the biochemical underpinnings of liver disease, ultimately aiming to develop effective therapies that can address the growing incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Bile Acid Metabolism: A Key Player in Liver Health
Understanding bile acid metabolism is vital for comprehending liver function and its implications in diseases, including liver cancer. Bile acids, produced by the liver, serve not only to emulsify fats for better nutrient absorption but also play a hormonal role in regulating various metabolic pathways. An imbalance in bile acid levels can lead to pathological states, including fibrosis and tumorous transformations.
Research connecting bile acid dynamics with liver cancer emphasizes the need for comprehensive studies into metabolic control mechanisms. By examining how components like YAP and FXR interact, scientists can uncover new aspects of liver physiology and pathology, fostering the development of therapeutic strategies aimed at restoring healthy bile acid metabolism and mitigating the risks associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Implications of YAP and FXR Research for Future Cancer Therapies
The emerging evidence linking YAP activation and FXR function to liver cancer opens new avenues for research and therapeutic intervention. As understanding of these molecular pathways deepens, it presents opportunities to devise drugs that can specifically target the dysregulation caused by YAP, restoring normal bile acid metabolism. This approach can significantly enhance liver health and reduce the incidence of liver cancer.
Future therapies that modulate the FXR pathway could revolutionize the treatment landscape for patients suffering from liver diseases. With ongoing research and clinical trials, the potential to develop effective pharmacological solutions that not only manage complications but also prevent the onset of hepatocellular carcinoma is becoming increasingly feasible. This is a promising prospect for liver cancer treatment and for improving the overall health outcomes in patients.
The Impact of Bile Acid Balance on Liver Disease
The intricate balance of bile acids is crucial for liver health, influencing everything from digestion to cancer risk. An imbalance often results in liver injury and can accelerate the progression towards diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma. Research has shown that alterations in bile acid composition can set off inflammatory responses that facilitate tumor development, thereby highlighting the need for maintaining bile homeostasis as a preventative measure.
Recent studies indicate that restoring bile acid balance through targeted therapies may provide protective benefits against liver disease progression. By examining how various factors affect bile acid dynamics, such as metabolic switches like YAP and FXR, scientists can pave the way for innovative approaches aimed at treating or preventing liver cancer effectively. This underscores the necessity for ongoing investigations into bile acid metabolism in health and disease.
Exploring the Intersection of Metabolism and Cancer in the Liver
The intersection of metabolism and cancer, particularly within the liver, is a burgeoning field of study. Researchers are increasingly focusing on how metabolic pathways intersect with cellular signaling processes, impacting the development of diseases like hepatocellular carcinoma. The complex interactions between bile acid production, YAP signaling, and FXR regulation exemplify the intricate networks that underlie liver health and disease.
By investigating how disturbances in metabolic signaling influence liver pathophysiology, researchers can uncover potential biomarkers for early detection and therapeutic targets for intervention. Advances in our understanding of bile acid metabolism and its connection to cancer will not only enhance our knowledge of liver biology but also contribute to the development of more effective preventative strategies against hepatocellular carcinoma.
The Future of Liver Cancer Research and Treatment
As research continues to unravel the complexities of bile acid metabolism and its association with liver cancer, the future holds promise for novel therapeutic interventions. Advances in molecular biology and targeted therapies could lead to groundbreaking treatments that address the underlying causes of hepatocellular carcinoma rather than merely mitigating symptoms. Understanding the role of key players like YAP and FXR will be central to these developments.
Ultimately, as we deepen our comprehension of liver cancer’s etiology through research into bile acid regulation and metabolic pathways, we pave the way for innovative treatment strategies that could change the paradigm of liver disease management. Promising findings from ongoing studies may soon translate into clinical applications, representing a hopeful outlook for those at risk of or currently battling liver cancer.
Frequently Asked Questions
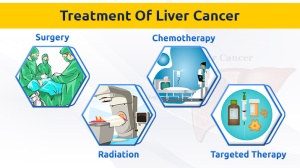
What are the most effective liver cancer treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
The most effective liver cancer treatment options for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) include surgical resection, liver transplantation, radiofrequency ablation, and systemic therapies such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy. Emerging treatments focus on targeting metabolic pathways influenced by bile acid metabolism and the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway.
How does bile imbalance relate to liver cancer treatment outcomes?
Bile imbalance significantly affects liver cancer treatment outcomes by contributing to liver injury and inflammation, which can exacerbate hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Treatments aiming to restore bile acid homeostasis, such as enhancing FXR function, are being explored to improve patient responses to therapy.
Can targeting YAP activation improve liver cancer treatment?
Yes, targeting YAP activation can improve liver cancer treatment by interrupting its repressive effects on FXR function. By promoting bile acid excretion and enhancing FXR signaling, we can potentially reduce tumor progression and enhance liver cancer treatment efficacy.
What role does FXR function play in liver cancer treatment strategies?
FXR function is critical in liver cancer treatment strategies as it regulates bile acid metabolism and prevents bile accumulation. Enhancing FXR activity can mitigate liver damage and inflammation, thereby improving the treatment outcomes for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
How can bile acid metabolism influence liver cancer treatment development?
Bile acid metabolism plays a significant role in liver cancer treatment development as it is intricately linked to liver health and disease. Pharmacological interventions that manipulate bile acid signaling, particularly through FXR activation, are being researched to create more effective liver cancer therapies.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance and Liver Cancer | A study highlights how bile imbalance can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Role of Bile Acids | Bile acids help digest fats and regulate metabolic processes, acting as hormones in the body. |
| YAP and FXR Relationship | YAP promotes tumor formation by interfering with the FXR bile acid sensor, leading to liver damage. |
| Study Insights | Activating FXR or inhibiting YAP’s repressor function can reduce liver damage and cancer progression. |
| Future Treatments | Research indicates potential pharmacological solutions that stimulate FXR for liver cancer treatment. |
Summary
Liver cancer treatment has gained new insights thanks to recent research that uncovers the link between bile acid imbalance and liver disease progression. Understanding the molecular mechanisms behind bile production and its regulation can pave the way for innovative therapies targeting liver cancer. Enhanced knowledge of the YAP and FXR interaction provides a promising avenue for developing treatments that could inhibit cancer progression by restoring normal bile function. As research continues, the potential for pharmacological interventions targeting these pathways offers hope for improving outcomes in liver cancer patients.